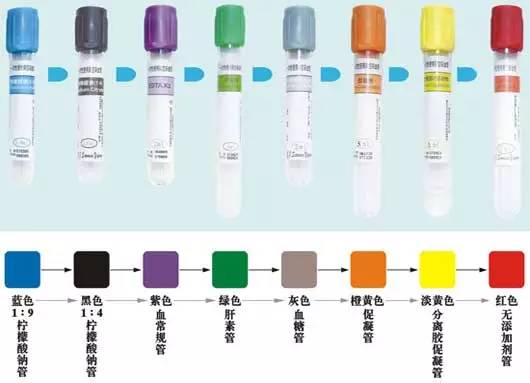
The different colors of the standard vacuum head cover and label represent various types of additives and test purposes, allowing you to select the appropriate test tube according to the requirements. Vacuum blood collection tubes are generally divided into the following types:
1. Red Cap Tube (Dry Vacuum Tube without Additives)
The inner wall of the blood collection tube is evenly coated with an agent (silicone oil) to prevent wall adherence. This tube utilizes the principle of natural blood coagulation to allow the blood to clot. After the serum has naturally precipitated, it is centrifuged for use. It is mainly used for serum biochemistry (liver function, kidney function, myocardial enzymes, amylase, etc.), electrolytes (serum potassium, sodium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, etc.), thyroid function, drug testing, AIDS testing, tumor markers, and serum immunity tests.
2. Orange-Red Cap Tube (Coagulation Tube)
(This tube is indeed orange-red but is very similar to the red cap tube mentioned above.)
The inner wall of the blood collection tube is evenly coated with silicone oil to prevent wall adherence, and a coagulant is added at the same time. The coagulant activates fibrinogen to turn soluble fibrin into insoluble fibrin polymer, forming a stable fibrin clot. If you need quick results, this coagulation tube can clot blood within 5 minutes and is generally used in emergency biochemistry.
3. Golden Yellow Cap Tube (Blood Tube Containing Inert Separating Glue and Coagulant)
The tube wall is siliconized and coated with a coagulant to accelerate blood coagulation and shorten the test time. Separating glue is added to the tube, which has a good affinity and isolates the liquid components (serum) from the solid components (blood cells) in the blood. After centrifugation, no oil droplets are generated in the serum, preventing blockage of the machine. This tube is primarily used for serum biochemistry (liver function, kidney function, myocardial enzymes, amylase, etc.), electrolytes, thyroid function, drug testing, AIDS testing, tumor markers, PCR, TORCH, and serum immunological testing.
4. Green Cap Tube (Heparin Anticoagulant Tube)
This tube contains heparin sodium or heparin lithium. Heparin is a mucopolysaccharide with sulfate groups that carries a strong negative charge, enhancing antithrombin III’s ability to inactivate serine proteases, thus preventing thrombin formation. It also has various anticoagulant effects, such as preventing platelet aggregation. Heparin tubes are generally used for emergency biochemistry, TORCH, and blood rheology tests. When testing sodium ions in blood samples, heparin sodium tubes should not be used, as they can affect test results. Additionally, they should not be used for white blood cell counting and classification, as heparin can cause white blood cell aggregation.
5. Purple Cap Tube (Tube Containing Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid and Its Salt)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an amino polycarboxylic acid that effectively chelates calcium ions in the blood. Chelating calcium removes it from the reaction point, preventing and stopping the endogenous or exogenous coagulation process, thereby preventing blood clotting. Compared to other anticoagulants, EDTA salts (2K, 3K, 2Na) have less impact on blood cell coagulation and morphology. This tube is used for general hematology (blood routine examination) and blood ammonia detection. It cannot be used for blood coagulation or trace element inspections.
6. Blue Cap Tube (Blood Tube Containing Sodium Citrate Anticoagulant)
Sodium citrate chelates with calcium ions in the blood sample to act as an anticoagulant. The anticoagulant-to-blood ratio is 1:9. This tube is primarily used in the fibrinolytic system (prothrombin time, thrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen). It is crucial to ensure a full blood volume (2 ml) during blood collection to guarantee accurate test results. After blood collection, the tube should be inverted and mixed 8-10 times immediately.
7. Black Cap Tube (Containing 0.109 mol/L Sodium Citrate)
The anticoagulant-to-blood volume ratio is 1:4, and it is generally used for erythrocyte sedimentation rate testing. If the anticoagulant ratio is too high, the blood may be diluted, which can accelerate the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. As with the blue cap tube, it is important to collect a full blood volume (2 ml) to ensure accuracy. After blood collection, it should also be inverted and mixed 8-10 times immediately.
8. Gray Cap Tube (Contains Potassium Oxalate/Sodium Fluoride)
Sodium fluoride is a weak anticoagulant that effectively prevents blood sugar degradation, making it an excellent preservative for blood sugar testing. When using this tube, be sure to invert and mix slowly. It is generally used for blood glucose testing and is not suitable for the urease method for determining urea, nor for alkaline phosphatase and amylase tests.
With the automated development of testing instruments such as blood cell analyzers, biochemical analyzers, and immune analyzers, the quantity and quality of blood sampling have gradually increased. To ensure the quality of test results, it is essential to distinguish not only between various vacuum blood collection tubes but also the blood collection sequence for each tube.
The colors of the caps on various vacuum blood collection tubes are international standards. It is recommended that the blood collection sequence for multiple tubes be: coagulation tube (blue) → blood routine tube (purple) → erythrocyte sedimentation rate (black) → biochemical tube (red, yellow). It is emphasized that the blood routine tube must be collected as the second tube due to its relationship with the blood coagulation mechanism. When blood culture is involved, the blood routine tube should be the third tube, as blood culture specimens require strict sterility, necessitating the use of blood culture tubes for the first collection. After blood collection, all tubes should be inverted 1-7 times without shaking. By paying attention to quality control before analysis, you can ensure that the test results are accurate and reliable.